✔ Competitive Pricing ✔ Quality Service ✔ Extensive Stock ✔ Experienced Staff
Reset Filter
 Price
PriceGuided Router Cutters
A Guide to Bearing Guided Router Cutters
With shaped router cutters (eg. bevel, roundover, dovetail etc), the fitting of an alternative larger diameter ball-bearing guide will often produce a different shape.
Straight cutters are also available as self-guiding cutters and are designed to follow the edge of the workpiece or a template fitted above or below it. Self-guided cutters are used for trimming, moulding or rebating. To achieve this, a ball-bearing guide is fitted, or a solid pin is brazed into the nose of the cutter.

Ball-Bearing Guided Router Cutters
Ball-bearing guides can be fitted either to the cutter shank, above the cutting edges or on a spigot machined on the end or nose of the cutter. As the ball-bearing diameter predetermines the width of the cut from the board edge, by changing the ball-bearing guide for one of a different diameter, the width or depth of the cut can be altered.
Ball-bearing guided cutters have the advantage of reducing the setting-up time, as the maximum width of the cut (e.g. rebate) or depth of cut (e.g. grooved edge) is fixed by the ball-bearing diameter. The ball-bearing guide or pin is run against the edge of the work, with a guide or template mounted above or below it.
This allows the cutter to follow a curved edge and avoids the need to use a side fence or parallel guide for straight edge work. The precision afforded by ball-bearing or pin-guided cutters is often critical when using the interlocking or matched profile scribing cutters.
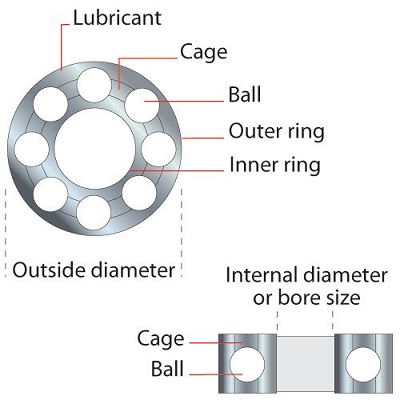
Ball-bearing guided cutters have an advantage over solid pin guided cutters, in that they produce less friction between the ball-bearing outer edge and the timber, reducing the risk of burning the edge of the workpiece. Ball-bearing guides are generally held in place by either a socket-headed screw or hexagonal nut. In most cases, a small washer is fitted, and should always be refitted when changing or refitting guide bearings.
Ballbearing guides for use on router cutters have shields fitted that reduce the amount of dust and dirt that can enter and clog the moving parts. Ball-bearing guides should be considered consumable and non-serviceable items and may need replacing during the life of the cutter. Never try to clean a ball-bearing with solvent, as this will dilute the grease lubricant. It is virtually impossible to replenish the grease, and any attempt to do so could prove dangerous or cause serious damage to the workpiece, as the ball-bearing is likely to collapse.
Pin Guided Router Cutters
Some basic shapes, such as ogees, core box, chamfer, rebating and trimming cutters are available with pin guides. These are used in similar applications as bearing guided types, yet are less versatile. They have the advantages that they can be used to shape or profile intricate shapes due to the smaller pin diameter. However, extra care is needed to prevent the edge of the workpiece or template from burning due to the frictional heat.

Find our full range of router cutters here, from top brands such as Trend and CMT.
You may also be interested in other Guides to Router Cutters
No items in this category





 01726 828 388
01726 828 388






